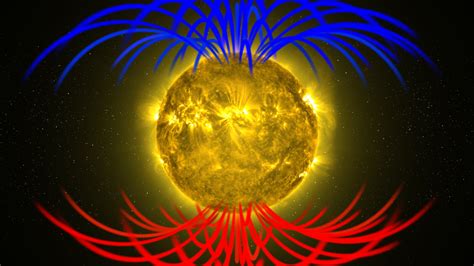
Every 11 years, the Sun undergoes a fascinating magnetic flip. Though this astronomical event might seem distant and abstract for most people, its repercussions are very close to home. The magnetic field reversal, part of the solar cycle, can influence space weather, impact Earth’s magnetic shield, and might even affect our climate in ways we’re just beginning to understand. The mechanism of the flip involves the Sun’s magnetic poles gradually weakening, trading places, and then building strength once again.
One interesting outcome of this solar phenomenon is its potential shielding effect against **galactic cosmic rays**. These high-energy subatomic particles, speeding through space near the speed of light, can be harmful to spacecraft and astronauts. When the Sun’s magnetic field flips, it creates a more complex and robust magnetic environment that can better deflect these cosmic rays. This effect, mentioned almost as an afterthought in many articles and obscured by various advertisements, is indeed profound. The importance of this shielding couldn’t be understated as it safeguards not just human endeavors in space, but also our technology and communication systems vulnerable to cosmic radiation.
While you might not feel the Sun’s magnetic flip directly, its influence permeates through several layers of our interaction with space. For instance, this event has **direct correlations** with the solar maximum, a period of peak solar activity marked by numerous sunspots, solar flares, and sometimes massive solar storms. Solar maximums bring about more frequent and intense auroras, stunning light displays caused by solar particles interacting with Earth’s magnetic field. These auroral shows, though a treat for the eyes, indicate heightened solar activity that could potentially disrupt communication satellites and power grids.
The intricate dance of the Sun’s magnetic field is a complex and gradual process, taking about five years to complete. This isn’t a sudden flip like a switch but a continuous rotation of the magnetic poles that “flips” once they traverse over the equator. Such a transition can make the orientation of the poles somewhat misaligned with Earth’s magnetic field temporarily, creating intriguing scientific observations and opportunities for research.
Beyond just space weather, there have been hypotheses linking solar activity to broader earthly phenomena. Some discussions suggest correlations between solar cycles and global events such as pandemics. This theory, albeit controversial and critiqued by many as
pseudoscience
implies that solar activity could influence biological mutations or even virus emergence. Although the science behind such claims remains speculative, it underscores the intricate and often surprising ways solar dynamics might intersect with life on Earth.
What might seem like an esoteric astronomical event affects everyone. For instance, the potential relation of solar activity with cloud formation and climate change is a rich area of research. A flip in the Sun’s magnetic field aligns with cycles that could slightly alter Earth’s climate. As our planet’s climate systems are influenced by myriad factors, from atmospheric chemistry to ocean currents, understanding the Sun’s role remains a frontier in climate science.

Leave a Reply